Despite being often mispronounced as “miliary disease,” the rare genetic condition known as milialar disease affects the skin and has potentially serious effects. Despite the fact that it is less well-known than other illnesses, it is crucial that those who are suffering from it have a complete understanding of the sickness.
Addressing Mispronunciation and Misunderstanding
There is a common pronunciation error and confusion between the terms miliary disease and “milialar disease.” But because these are two different medical diseases, it is crucial to distinguish between the two. The term “miliary disease” usually refers to a type of illness marked by small, millet-sized nodules in the lungs or other organs, which is frequently brought on by tuberculosis or specific fungi. However, “milialar disease” is an uncommon genetic skin condition with distinct symptoms.
What is Milialar Disease?
Milialar disease, often called “milialar keratosis,” is a rare hereditary condition that mostly impacts the skin. It usually manifests in early childhood or adolescence and is inherited. Mutations in particular genes that are in charge of regulating the growth of the epidermis, the skin’s outermost layer, cause this illness.
Genetic Causes
Similar illness is a hereditary ailment because of its genetic foundation. Autosomal dominant mutations in the KRT5 or KRT14 genes are responsible for the majority of cases. These genes give instructions on how to make proteins that are necessary for maintaining the skin’s structural integrity.
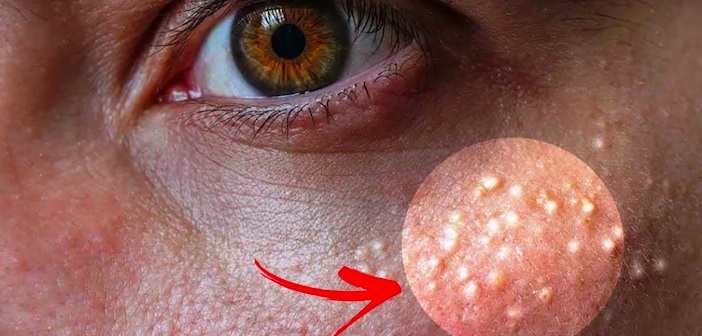
The development of the skin’s outer layer is hampered by mutations in these genes. A variety of skin abnormalities may result from this, such as the development of tiny, hard, white, or red papules (small bumps), which may be encircled by red, swollen skin.
Impact on the Skin
Miliary illness primarily affects the skin, yet each individual will experience it differently and experience the disease to a different degree. Typical signs of skin conditions include:
Papules and Blisters: The emergence of cutaneous papules and blisters is the defining feature of miliary illness. These may appear on the elbows, knees, soles of the feet, palms of the hands, and other parts of the body.
Changes in Nails: The illness can also have an impact on nails, causing nail dystrophy or an abnormal growth of nails.
Scalp Participation: In some circumstances, the scalp may be impacted, causing hair loss and skin thickness.
Possibility of complications Miliary illness in extreme situations can result in consequences like infection, open sores, and movement issues because of the skin.
Potential for consequences: Miliary disease has the potential to cause consequences in severe cases, including infection, open sores, and difficulties moving owing to skin tightness and blistering.
Diagnosis and symptoms
The fact that similar sickness is a rare ailment is one of its difficulties. It’s possible that many medical professionals are unfamiliar with it, which could result in delayed or incorrect diagnoses. As a result, it’s critical for anyone experiencing symptoms to speak with a dermatologist or geneticist.
Typical Symptoms
Miliary illness can have various effects in addition to its primary skin manifestations. Blisters and papules appearing on the skin are common signs.
- Skin that is thicker, redder, or inflamed around the blisters.
- Anomalies in the nails, such as thickness, ridges, or pitting.
- Involvement of the scalp resulting in skin thickening and hair loss.
- Discomfort brought on by skin lesions, including pain or itching.
Diagnostic Issues
Miliary disease can be challenging to diagnose due to its rarity and similarities to other skin conditions. Medical professionals may need to carry out a number of procedures, including genetic testing and skin biopsies, to confirm the diagnosis. These examinations can help in identifying the particular gene changes that result in the disease.
It is crucial to speak with a doctor who has experience with uncommon genetic skin problems. To help people and their families comprehend the genetic consequences of the illness and its inheritance pattern, genetic counseling may also be advised.
Treatment and Management
Miliary illness is generally managed by addressing the symptoms and side effects brought on by the ailment. There is no treatment, but there are a few options to think about:
Treatment Options
Topical treatments: Emollients and moisturizers are two examples of topical treatments that dermatologists could use to treat dry, itchy skin.
Pain Management: Anti-inflammatory drugs or painkillers may be recommended to treat the pain and inflammation brought on by skin lesions.
Taking Care of Blisters: There are methods for treating blisters and lowering the chance of infection. This can entail carefully cleaning and treating blisters.
Nail Care: For nail anomalies, care and maintenance techniques may be advised, such as using specific nail treatments and shielding the nails from harm.
Genetic counseling can help people and their families understand the genetic underpinnings and pattern of inheritance of common diseases.
Permanent Management
Miliary illness requires continuing therapy because it is a chronic disorder. This entails routine follow-up consultations with dermatologists and other experts. These medical professionals can keep an eye on the illness, modify treatment plans as necessary, and offer assistance in handling potential physical and mental difficulties.
The Effect on Everyday Life
A person’s daily life can be greatly affected by having a similar ailment. The illness can have severe physical and emotional implications.
Physical and Emotional Effects
Miliary illness can have uncomfortable and painful physical side effects, such as blistering, inflammation, and irregularities in the nails. These symptoms may make it difficult to move around and interfere with normal tasks. Complications including skin infections might worsen the quality of life in extreme situations.
It is important to recognize the emotional toll that having a rare hereditary skin illness has on a person. Due to the apparent aspect of the disorder, people with similar diseases may experience emotions of self-consciousness, melancholy, and worry. This emphasizes how crucial it is to offer individuals who are afflicted psychological support and emotional support.
Personal Stories
It is crucial to relate the personal experiences of others suffering with similar diseases in order to make the illness more approachable. These accounts can shed light on the difficulties people encounter, their coping mechanisms, and their fortitude.
One such tale is Sarah’s, who was diagnosed with a similar illness in her early adolescence. She describes the process she went through to learn how to control the disease, from coping with the bodily symptoms to getting emotional help. Sarah’s experience serves as a testament to the perseverance of those with rare genetic illnesses and the value of awareness-building.
Raising Awareness
Miliary illness requires recognition and care despite its rarity. The effects of uncommon diseases extend beyond the individuals who are afflicted; they have an impact on their families, friends, and communities as well. Increasing awareness may result in better resources, research, and support for people coping with similar diseases.
Strength of Awareness
For a number of reasons, increasing public awareness of uncommon diseases like Miliary disease is essential.
Improved awareness may result in an earlier diagnosis and course of action, which is frequently essential in controlling the condition and avoiding consequences.
Support and Resources: With greater awareness, persons affected by similar diseases may have access to more resources and support services.
Research advances: Research attempts to better understand the ailment, identify viable therapies, and hunt for a cure can be sparked by increased awareness.
Reducing Stigma: Increasing awareness can aid in lowering the stigma attached to skin disorders that are visible, assisting people on their path to self-acceptance.
How to Participate
There are various things that people can do to help the cause of miliary illness awareness:
Information Exchange: To raise awareness of this disease, share educational materials and blog entries like this one with your network.
Look for and support organizations that are focused on rare skin conditions. These groups frequently offer helpful advice, assistance, and financing for study.
Take Part in Awareness-Raising Campaigns: Participate in activities and initiatives to raise awareness of rare diseases that are sponsored by advocacy groups.
Donate to fundraising initiatives that promote research and resources for people with similar diseases.
Conclusion
Despite the frequent mispronunciation of its name, miliary illness is a rare genetic skin condition that can have a serious effect on people who are infected. It is essential to distinguish this ailment from “military disease” and to increase awareness of this issue. For people with a similar ailment, early diagnosis, efficient management, and emotional support are crucial.
We can encourage understanding, compassion, and support for people who live with uncommon genetic skin problems by exchanging information and personal experiences. The first step in enhancing the quality of life for persons suffering from uncommon diseases and other common ailments is raising awareness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.What is Miliary Disease, exactly?
A. Milialar Keratosis, sometimes referred to as Milialar Disease, is a rare inherited skin condition. Small, firm, white or red papules (bumps), which may be encircled by red, irritated skin, appear as its primary skin-related symptom. This inherited disorder typically manifests during childhood or adolescence.
Q. How is Milialar Disease Different from Miliary Disease?
A. It’s common to mispronounce Milialar illness as “miliary disease.” These are separate conditions, though. A pattern of illness known as “miliary disease” is characterized by small, millet-sized nodules in the lungs or other organs, which are frequently brought on by tuberculosis or specific fungi. In contrast, Milialar Disease is a skin condition.
Q. What Causes Milialar Disease?
A. Mutations in the KRT5 or KRT14 genes, which are in charge of maintaining the skin’s structural integrity, are the main contributors to Milialar Disease. The epidermis, the skin’s outer layer, develops abnormally as a result of these gene abnormalities.
Q. What Are the Common Symptoms of Milialar Disease?
A. The appearance of blisters and papules on the skin, nail abnormalities (such as pitting, ridges, or thickening), involvement of the scalp resulting in hair loss and thicker skin, and discomfort, pain, or itching brought on by skin lesions are all common symptoms of Milialar Disease.
Q. How is Milialar Disease Diagnosed?
A. Due to its rarity, Milialar Disease might be difficult to diagnose. To confirm the diagnosis, it frequently takes specialized testing, such as skin biopsies and genetic testing. It is crucial to seek the advice of a dermatologist or genetics expert.